How to deploy a single solution for all legacy, on-premises, and cloud applications.
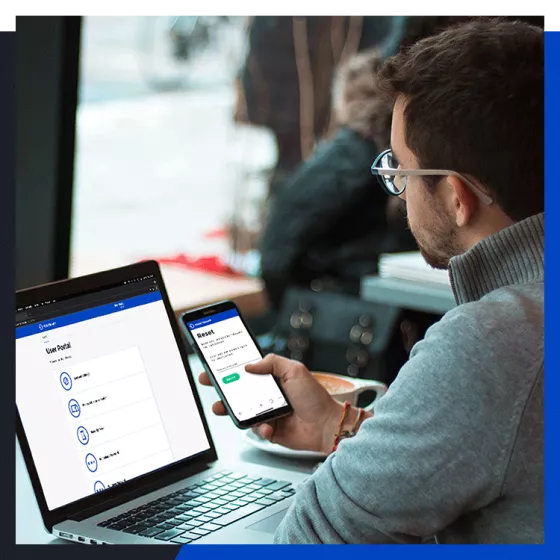
With an ever-evolving landscape, most organizations face an infrastructure that has grown into a hybrid model, consisting of a mix of legacy applications, on-premises, and cloud services. That also brings along a proliferation of various accounts, identities, and login methods that are extremely challenging to manage centrally, let alone harmonize easily. Is it even possible to gather all applications under a single digital identity and protect everything with MFA?
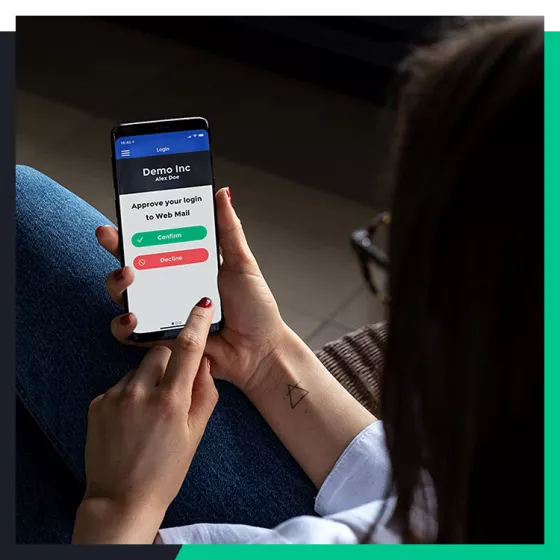
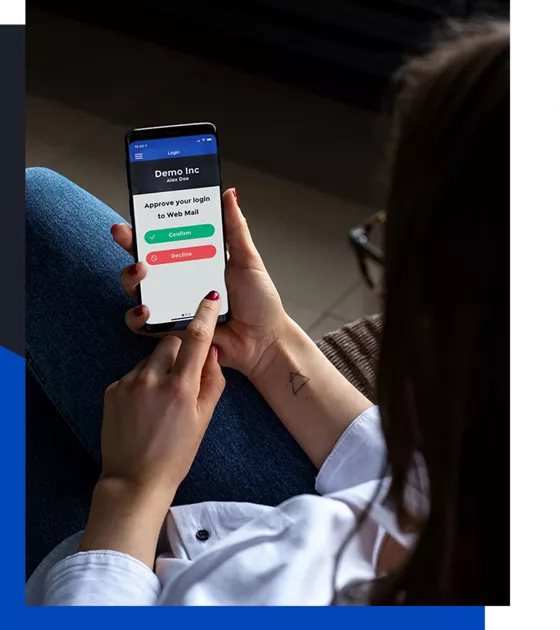
In this webinar, our experts will discuss the challenges with the modern hybrid infrastructure and how you can enable multi-factor authentication with single sign-on for all your apps, whether cloud-based or on-premises legacy applications. Our experts will discuss what you should consider when choosing a comprehensive MFA solution, how to deploy it, and what are the best practices for a successful rollout.
In this webinar you will learn:
- What are the challenges to implementing strong authentication in a hybrid infrastructure?
- What you need to take into consideration
- How to deploy one MFA solution for all your users and applications